Difference between revisions of "Example 3: Beer Distribution with Limited Routes"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category: Analytica Optimizer Guide]] | ||
[[Category: Beer Distribution model]] | [[Category: Beer Distribution model]] | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
The restriction of possible routes can be cumbersome in some optimizing environments. As this example will show, in Analytica, it is a simple matter of changing the dimension of the decision array. | The restriction of possible routes can be cumbersome in some optimizing environments. As this example will show, in Analytica, it is a simple matter of changing the dimension of the decision array. | ||
| + | |||
==Model Description== | ==Model Description== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
==Setting Up the Model== | ==Setting Up the Model== | ||
| − | To explore and follow this example in Analytica, run the | + | To explore and follow this example in Analytica, run the <code>Beer Distribution LP 3.ana</code> model in the Optimizer Examples folder. |
In this section, we start with the model from Example 2, detailing changes only. | In this section, we start with the model from Example 2, detailing changes only. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
First, we create an index of approved routes. These are specific combinations of '''Brewery''' and '''Market.''' | First, we create an index of approved routes. These are specific combinations of '''Brewery''' and '''Market.''' | ||
| − | [[File:4-3-1.png|300px]] | + | :[[File:4-3-1.png|300px]] |
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | ['Fairfield North','Fairfield South','Fairfield West', | + | Index Route := |
| − | 'Fort Collins North','Fort Collins South', | + | ['Fairfield North', 'Fairfield South', 'Fairfield West', |
| + | 'Fort Collins North', 'Fort Collins South', | ||
'Jacksonvile East', | 'Jacksonvile East', | ||
| − | 'Merrimack North','Merrimack East', | + | 'Merrimack North', 'Merrimack East', |
| − | 'St Louis North','St Louis East']</ | + | 'St Louis North', 'St Louis East'] |
| + | </pre> | ||
'''Redefine the Decision input array''' | '''Redefine the Decision input array''' | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
Make sure to also edit the Intrinsic Indexes list. Remove '''Brewery''' and '''Market''', and add '''Route''' to the list. | Make sure to also edit the Intrinsic Indexes list. Remove '''Brewery''' and '''Market''', and add '''Route''' to the list. | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | + | Variable Shipment_Quantity := Array(Route, 1) | |
| + | Shipment_Quantity attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Route] | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
'''Redefine the Objective and its inputs''' | '''Redefine the Objective and its inputs''' | ||
The Objective representing '''Total Distribution Cost''' should now sum over the '''Route''' index instead of '''Brewery''' and '''Market'''. | The Objective representing '''Total Distribution Cost''' should now sum over the '''Route''' index instead of '''Brewery''' and '''Market'''. | ||
| − | + | :<code>Objective Total_Dist_Cost := Sum(Shipment_Quantity*Dist_per_case, Route)</code> | |
| + | |||
All inputs to '''Total Distribution Cost''' should be also dimensioned by '''Route'''. We redefine the '''Distance''' array using corresponding values from the original table. | All inputs to '''Total Distribution Cost''' should be also dimensioned by '''Route'''. We redefine the '''Distance''' array using corresponding values from the original table. | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | Table(Route)(1.8,2.2,0.1,0.3,1.2,0.6,1.2,0.2,0.5,0.8) </ | + | Variable Distance := |
| + | Table(Route)(1.8, 2.2, 0.1, 0.3, 1.2, 0.6, 1.2, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | Original Distance Array [[File:4-3-2a.png|400px]] | + | Original Distance Array: |
| + | :[[File:4-3-2a.png|400px]] | ||
| − | Redefined Distance Array [[File:4-3-2b.png|300px]] | + | Redefined Distance Array: |
| + | :[[File:4-3-2b.png|300px]] | ||
'''Creating Index Maps''' | '''Creating Index Maps''' | ||
| Line 53: | Line 65: | ||
Create a new variable titled '''Route / Brewery map'''. | Create a new variable titled '''Route / Brewery map'''. | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| + | Variable Route_Brewery_map := Table(Route) | ||
('Fairfield', 'Fairfield', 'Fairfield', | ('Fairfield', 'Fairfield', 'Fairfield', | ||
'Fort Collins', 'Fort Collins', | 'Fort Collins', 'Fort Collins', | ||
'Jacksonville', | 'Jacksonville', | ||
'Merrimack', 'Merrimack', | 'Merrimack', 'Merrimack', | ||
| − | 'St Louis', 'St Louis' )</ | + | 'St Louis', 'St Louis' ) |
| + | </pre> | ||
Create a new variable titled '''Route / Market map'''. | Create a new variable titled '''Route / Market map'''. | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| + | Variable Route_Market_map :=Table(Route) | ||
('North','South','West','North','South', | ('North','South','West','North','South', | ||
| − | 'East','North','East','North','East')</ | + | 'East','North','East','North','East') |
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | [[File:4-3-3.png|500px]] | + | :[[File:4-3-3.png|500px]] |
'''Using Aggregate()''' | '''Using Aggregate()''' | ||
| − | The [ | + | The [[Aggregate]] function can use these maps to create aggregated sums. This allows us to convert '''Shipment Quantities''' from the fine index ('''Route''') to the coarse target indexes ('''Brewery''' or '''Market'''). |
| + | |||
| + | The basic syntax of the [[Aggregate]]Function is: | ||
| + | :<code>Aggregate(input_array, map, fine_index, target_index)</code> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Aggregate Shipment Quantities''' | '''Aggregate Shipment Quantities''' | ||
| Line 79: | Line 96: | ||
Create a new variable titled '''Total Shipments from Breweries''' | Create a new variable titled '''Total Shipments from Breweries''' | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | + | Variable Ship_from_Brewery := | |
| − | Aggregate(Shipment_Quantity, Route_Brewery_map, Route, Brewery)</ | + | Aggregate(Shipment_Quantity, Route_Brewery_map, Route, Brewery) |
| + | </pre> | ||
Create a new variable titled '''Total Shipments to Markets''' | Create a new variable titled '''Total Shipments to Markets''' | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | Aggregate(Shipment_Quantity, Route_Market_map, Route, Market)</ | + | Variable Ship_to_Market := |
| + | Aggregate(Shipment_Quantity, Route_Market_map, Route, Market) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
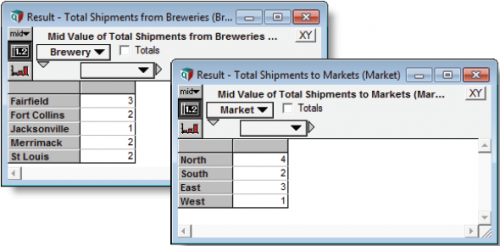
You can evaluate the aggregated arrays to verify that they represent '''Shipment Quantities''' aggregated by '''Brewery''' and '''Market'''. Input Quantities are 1 for each '''Route''', so these aggregated sums represent the number of routes associated with each '''Brewery''' or '''Market'''. | You can evaluate the aggregated arrays to verify that they represent '''Shipment Quantities''' aggregated by '''Brewery''' and '''Market'''. Input Quantities are 1 for each '''Route''', so these aggregated sums represent the number of routes associated with each '''Brewery''' or '''Market'''. | ||
| − | [[File:4-3-4.png|500px]] | + | :[[File:4-3-4.png|500px]] |
'''Edit Constraint Inputs''' | '''Edit Constraint Inputs''' | ||
| Line 95: | Line 115: | ||
Edit the '''Supply Constraint''' to use '''Total Shipments from Breweries''' as an input. '''Brewery''' is still an intrinsic index for this node. | Edit the '''Supply Constraint''' to use '''Total Shipments from Breweries''' as an input. '''Brewery''' is still an intrinsic index for this node. | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | Supply Constraint attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Brewery]</ | + | Constraint Supply_Constraint := Ship_from_brewery <= Production_Limits |
| + | Supply Constraint attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Brewery] | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Edit the '''Demand Constraint''' to use '''Total Shipments to Markets''' as an input. '''Market''' is still an intrinsic index for this node. | Edit the '''Demand Constraint''' to use '''Total Shipments to Markets''' as an input. '''Market''' is still an intrinsic index for this node. | ||
| − | + | <pre style="background:white; border:white; margin-left: 1em;"> | |
| − | + | Constraint Demand_Constraint := Ship_to_market >= Delivery_Target | |
| + | Demand Constraint attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Market] | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
== Checking the Result == | == Checking the Result == | ||
| Line 107: | Line 131: | ||
This is now a two-dimensional array indexed by the intrinsic '''Route''' index and the extrinsic '''World Series Winner''' index. | This is now a two-dimensional array indexed by the intrinsic '''Route''' index and the extrinsic '''World Series Winner''' index. | ||
| − | [[File:4-3-5.png|500px]] | + | :[[File:4-3-5.png|500px]] |
| − | [[File:4-3-6.png|600px]] | + | :[[File:4-3-6.png|600px]] |
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| + | * [[Arrays and Indexes]] | ||
| + | * [[Index..Do]] | ||
| + | * [[Var..Do]] | ||
| + | * [[Sum]] | ||
| + | * [[Aggregate]] | ||
* [[Example Models and Libraries]] | * [[Example Models and Libraries]] | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 29 March 2016
The restriction of possible routes can be cumbersome in some optimizing environments. As this example will show, in Analytica, it is a simple matter of changing the dimension of the decision array.
Model Description
In the previous examples, we allowed all five Breweries to ship to all four Markets, presenting 20 possible routes. In this example, we confine the shipments to 10 chosen routes and disallow the rest.
Setting Up the Model
To explore and follow this example in Analytica, run the Beer Distribution LP 3.ana model in the Optimizer Examples folder.
In this section, we start with the model from Example 2, detailing changes only.
Create a Route Index
First, we create an index of approved routes. These are specific combinations of Brewery and Market.
Index Route :=
['Fairfield North', 'Fairfield South', 'Fairfield West',
'Fort Collins North', 'Fort Collins South',
'Jacksonvile East',
'Merrimack North', 'Merrimack East',
'St Louis North', 'St Louis East']
Redefine the Decision input array
In previous examples, we defined the Decision input as a two-dimensional array. In this example we redefine it to be a one-dimensional array along the index of approved routes. Once again, we can insert a dummy value of 1 for the non-optimized quantities since they are not used anywhere else in the model.
Edit the Intrinsic Indexes list
Make sure to also edit the Intrinsic Indexes list. Remove Brewery and Market, and add Route to the list.
Variable Shipment_Quantity := Array(Route, 1) Shipment_Quantity attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Route]
Redefine the Objective and its inputs
The Objective representing Total Distribution Cost should now sum over the Route index instead of Brewery and Market.
Objective Total_Dist_Cost := Sum(Shipment_Quantity*Dist_per_case, Route)
All inputs to Total Distribution Cost should be also dimensioned by Route. We redefine the Distance array using corresponding values from the original table.
Variable Distance :=
Table(Route)(1.8, 2.2, 0.1, 0.3, 1.2, 0.6, 1.2, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8)
Original Distance Array:
Redefined Distance Array:
Creating Index Maps
Constraint arrays do not change indexes in the new model. Production Limits still apply to Breweries, and Delivery Targets still apply to Markets. But the Shipment Quantities array no longer contains these indexes. To solve this dilemma, we start by making index maps relating the Route index to Brewery and Market. An index map is a one-dimensional array that associates a coarse index with a fine index. The map uses the fine index as its dimension and lists corresponding elements of the coarse index.
Create a new variable titled Route / Brewery map.
Variable Route_Brewery_map := Table(Route)
('Fairfield', 'Fairfield', 'Fairfield',
'Fort Collins', 'Fort Collins',
'Jacksonville',
'Merrimack', 'Merrimack',
'St Louis', 'St Louis' )
Create a new variable titled Route / Market map.
Variable Route_Market_map :=Table(Route)
('North','South','West','North','South',
'East','North','East','North','East')
Using Aggregate()
The Aggregate function can use these maps to create aggregated sums. This allows us to convert Shipment Quantities from the fine index (Route) to the coarse target indexes (Brewery or Market).
The basic syntax of the AggregateFunction is:
Aggregate(input_array, map, fine_index, target_index)
Aggregate Shipment Quantities
Now we can create suitable inputs for the Constraint nodes.
Create a new variable titled Total Shipments from Breweries
Variable Ship_from_Brewery :=
Aggregate(Shipment_Quantity, Route_Brewery_map, Route, Brewery)
Create a new variable titled Total Shipments to Markets
Variable Ship_to_Market :=
Aggregate(Shipment_Quantity, Route_Market_map, Route, Market)
You can evaluate the aggregated arrays to verify that they represent Shipment Quantities aggregated by Brewery and Market. Input Quantities are 1 for each Route, so these aggregated sums represent the number of routes associated with each Brewery or Market.
Edit Constraint Inputs
Edit the Supply Constraint to use Total Shipments from Breweries as an input. Brewery is still an intrinsic index for this node.
Constraint Supply_Constraint := Ship_from_brewery <= Production_Limits Supply Constraint attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Brewery]
Edit the Demand Constraint to use Total Shipments to Markets as an input. Market is still an intrinsic index for this node.
Constraint Demand_Constraint := Ship_to_market >= Delivery_Target Demand Constraint attribute Intrinsic Indexes := [Market]
Checking the Result
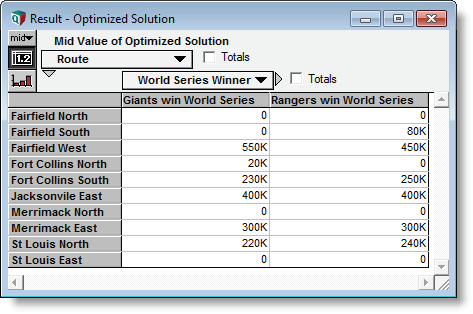
Evaluate the Optimized Solution array to see the result for the limited route example. This is now a two-dimensional array indexed by the intrinsic Route index and the extrinsic World Series Winner index.
See Also





Enable comment auto-refresher